
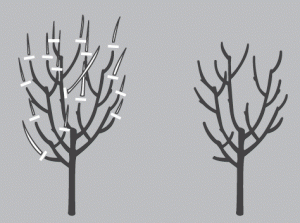

Pushes production closer to main branches. Continual spur pruning eventually leads to congestion. SPUR PRUNING - Shorten laterals to increase fruiting side shoots. Spur bearers – fruit on 3 year wood or older. TYPES OF FRUIT TREES APPLE PEACH PEAR QUINCE PLUM CHERRY NECTARINE APRICOT MULBERRY FIGS PERSIMMONĪPPLE TREE Self fertile. Try to regain form, if not feasible, replace tree. TRAINED FORMS - Reduce growth and thin congested spurs.BROKEN – Cut branches or exposed bark are susceptible to water penetration.Overcrowding creates stagnant air, poor circulation. CROWDED OR CROSSING - Touching branches lead to bark/insect damage.Cut tree below infected area where healthy tissue resumes. Heavily cankered trees should be discarded. ROOT Best done on young trees in winter.FRUITING HABIT Heavy crops produce small unsatisfactory fruits / biennial bearing Blossom thinning 10 days after blossom pinch out 9 of every 10 blossoms Fruit thinning.BALANCE Younger wood produces finer fruit Apple & pear on 2 year wood Sour cherry, peach & nectarine on previous year Plum, sweet cherry & apricot on 2 year and older.Hard pruning lessens the amount of flower buds being served by tree and allows for better production from the remaining bugs. HARD VS LIGHT Prune weak growth hard and strong growth light.įRUIT TREE FORMS Bush Pyramid Cordon, Single, double or triple Half standard Dwarf pyramid Standard Spindle bush Fan Palmette Espalier Stepover.

FRUIT TREE PRUNING Elisa Clark Horticulturist, CLT, CNP, Master Gardener Flutterby Gardens Landscaping 571-2170 North End Organic Nursery 389-4769


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
